- By Admin
- In Health and Tips,
- Posted September 11, 2025
Nerve Stroke: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms & Prevention and Treatment
Introduction
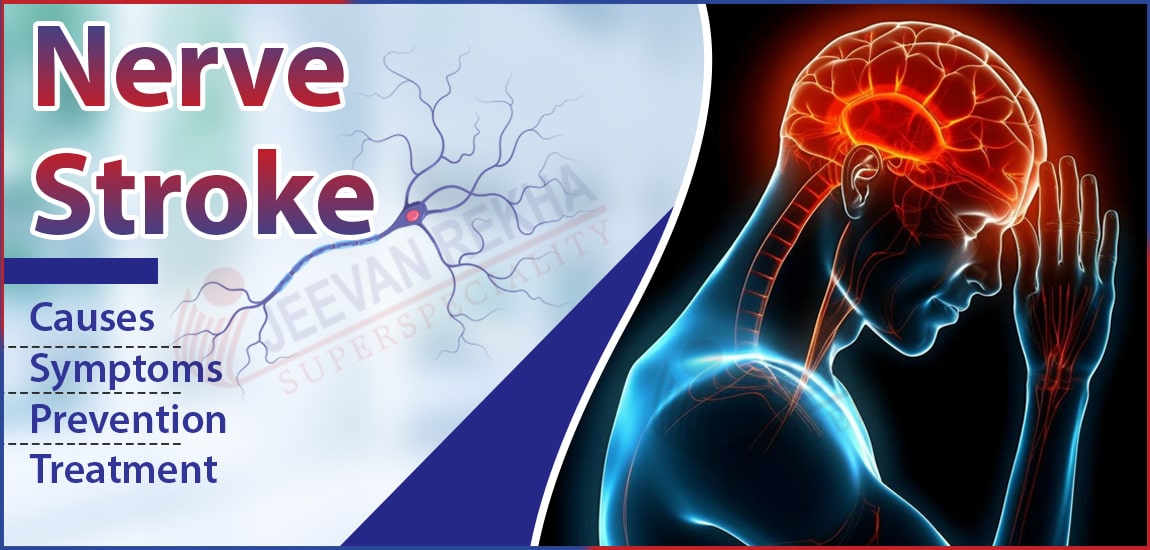
Nerve stroke, or simply a stroke, is a serious condition when the blood flow to the brain is interrupted, damaging the nerve cells and brain tissues. While the causes consist of blocked arteries or somehow ruptured blood vessels, the symptoms of nerve stroke are usually sudden: weakness, confusion, or difficulty in speaking.
One should know the risk factors for stroke, like hypertension, smoking, and diabetes, for prevention. Timely care, treatment, and a changed lifestyle serve as an effective nerve stroke treatment that would ensure recovery and improvement in the patient's quality of life.
What Is a Nerve Stroke?
Usually referred to as a stroke, a Nerve stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when an artery that supplies blood to the brain is blocked or when blood flow is reduced to any part of the brain. It results in brain tissues being starved of oxygen and nutrients, leading to damage or destruction of brain cells. This loss of nerve function controls very essential activities like movement, speech, memory, and coordination.
What are the causes of a nerve stroke?
The causes of stroke are linked to conditions affecting blood flow to the brain, either by blockage or rupture of blood vessels; an understanding of stroke causes can aid in early prevention and management on time.
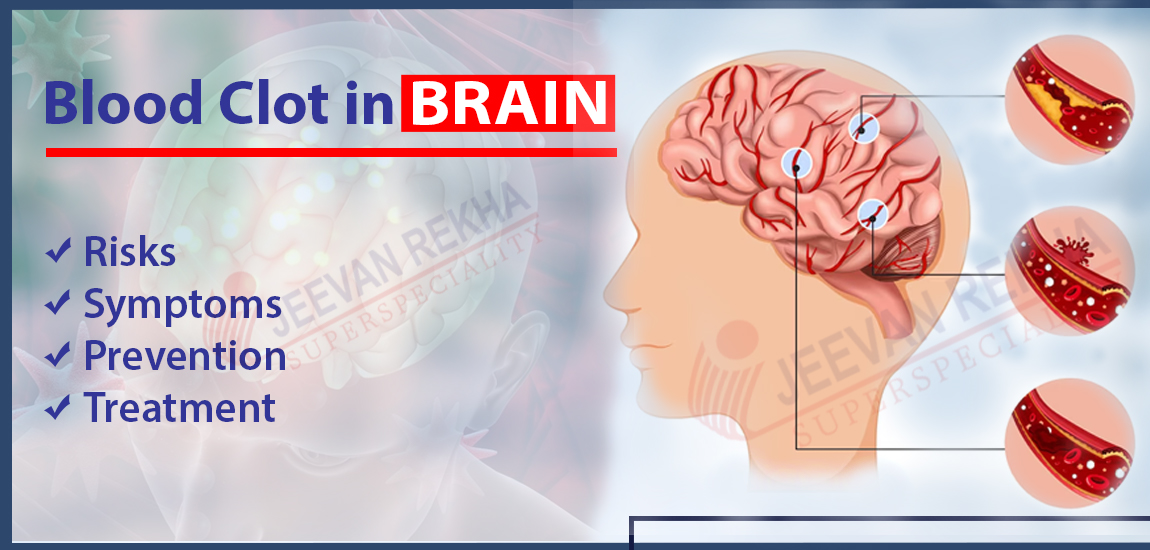
- Blocked Arteries (Ischemic Stroke): The most common cause of a stroke is when blood clots or fatty deposits (plaque) block the flow of blood to the brain. Ruptured
- Blood Vessel (Hemorrhagic Stroke): A wrong blood vessel in the brain will rupture and hemorrhage, leading to pressure on the brain tissues.
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Also called a mini-stroke, this occurs when blood flow to the brain is temporarily blocked; this is a sign that a major stroke could soon follow.
- High Blood Pressure: Long-term hypertension species are weakened over time, making them liable to be blocked or ruptured and directly increasing stroke chances.
- Heart and Blood Disorders: Conditions like atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and clotting disorders cause clots to travel to the brain and lead to a stroke.
What are the symptoms of a nerve stroke?
Symptoms of a nerve stroke usually occur suddenly and can differ depending on the brain area affected. Early recognition of these warning signs is very important for an emergency admission and proper treatment.
- Sudden Numbness or Weakness: A stroke usually brings about weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, usually on just one side of the body.
- Difficulty Speaking or Understanding Speech- One suddenly gets difficulty producing clear speech or understanding others.
- Problems With Vision: A stroke is possibly indicated by blurred or double vision, or a sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Problems With Coordination or Balance: As a consequence of the stroke, you may experience dizziness, loss of balance, or wavering while walking.
- Severe Headache: Those big-headed pains that come out of nowhere are quite classic for hemorrhagic stroke.
- Confusion and Trouble Thinking: Disorientation, loss of memory, and difficulties in understanding instructions may be experienced after a stroke.
You Can Read Also: Kidney Infection: Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
What are the risk factors for stroke?
The risk factors for a stroke are conditions, habits, or health issues that increase the odds of one incurring a stroke. Recognizing these factors allows one to consider preventive measures and may reduce the incidence of stroke.
- High Blood Pressure: It is the paramount risk factor and can damage arteries, so they can get blocked or ruptured easily.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar damages blood vessels and initiates the deposition of fatty materials, leading to stroke.
- Smoking or Alcohol: Smoking leads to thickening of the blood and damage to the arteries, while excessive consumption of alcohol raises the blood pressure. Both habits lead to an increased risk of stroke.
- High cholesterol embolism with fatty deposits in the arteries may stop blood flow toward the brain.
- Lack of Exercise or Being Overweight: Obesity and lack of physical activity insidiously encourage hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease, all of which are risk factors for stroke.
- Heart Conditions: Thrombi in the parametric region may arise secondary to atrial fibrillation, heart failure, or valvular diseases and embolize to the cerebral arteries.
- Age and Family History: With advancing age, the recognized risk of stroke increases, and persons with a positive family history remain more highly vulnerable.
- Unhealthy Diet: Excessive intake of salt, processed foods, or saturated fats produces hypertension and cholesterol, thereby increasing the risk of stroke.
How to Prevent Nerve Stroke?
Prevention of nerve stroke includes managing health conditions and lifestyle to keep the possibility of stroke down to a minimum. Working on the root cause of a stroke will prevent its occurrence, while staying away from activities that may bring about a stroke will do the same.
- Maintain a Healthy Blood Pressure: Normal blood pressure is an effective preventive measure against stroke.
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Through diet, exercise, and medicines, you can manage diabetes well and thereby preserve blood vessels from injury.
- Quit Smoking and Reduce Alcohol Intake: Limit damage caused to artery walls and clotting in the blood.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: More fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins; less salt and unhealthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Thirty minutes of exercise promotes good circulation, controls body weight, and lowers the chances of a stroke.
- Manage Cholesterol: Regular monitoring, diet modification to lower cholesterol buildup in the arteries.
- Treat Heart Problems: Timely treatment of atrial fibrillation, heart failure, or other cardiac problems decreases the potential for clot formation, leading to stroke.
You Can Read Also: Alcoholic vs. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver: Understanding the Key Differences
Treatment Option for Nerve Stroke?
Treatments of stroke depend upon the type of stroke, its severity, and how quickly the patient gets medical help. The sooner the treatment, the less the damage caused to the brain and the greater the chances of good recovery.
- Emergency Treatment: For ischemic stroke clot-busting medications such as tPA are given within a defined period to dissolve the clot and restore circulation.
- Clot Removal: There might be situations in which doctors will try to remove a clot from a brain artery by doing a mechanical thrombectomy.
- Surgery for Hemorrhagic Stroke: When a hemorrhage occurs in the brain, it may require surgical intervention to repair ruptured blood vessels, evacuate blood, or relieve intracranial pressure.
- Rehabilitation Therapy: All these treatments were meant to help patients regain motor skills, coordination, speech, and the activities of daily living after stroke.
- Recovery Medication: Sometimes, an anticoagulant, blood pressure-lowering drug, or a cholesterol lowering drug is given to the patient with hopes that it will prevent the next stroke.
- Lifestyle Change: Healthy lifestyle changes-exercising, eating healthy food, and managing stress-will contribute to immediate recovery and prevention of another stroke alongside medical treatment.
When to See a Doctor?
Knowing the right-time treatment for a nerve stroke is important since prompt treatment could lead to life-saving or could hinder someone from being a life of someone. Medical attention should be sought immediately should any of these symptoms occur:
Symptoms of Stroke
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness: Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arms, or legs, especially if present on one side of the body, should be taken for emergency medical care.
- Problems With Speech or Understanding: There should be a cry for urgent medical care if there is a sudden slur in speech or an inability to produce any words or comprehend what is being said.
- Vision Problems: Warning signs from the eyes include blurred vision, double vision, or sudden loss of vision in either eye.
- Severe Headache: Sudden onset of headache that is so severe and without a clear cause could be an indication of a hemorrhagic stroke. Such a headache should receive immediate attention.
- Loss of Balance or Coordination: Don't disregard sudden dizzy spells, bad walking, or balance loss.
- Confusion or Trouble Thinking: A sudden bout of disorientation, forgetfulness, inability to take in simple information, or to process simple information could well be the signs of a stroke.
Conclusion
To conclude, nerve stroke is an emergency that requires timely diagnosis, expeditious treatment, and precautionary interventions. Knowing the causes of stroke, along with the symptoms of nerve stroke and risk factors for stroke, all help minimize its occurrence.
The Neurology Department provides the best treatment for nerve stroke, in which timely treatment helps in better recovery. Jeevan Rekha Hospital offers the best neurology facilities and expert stroke management so that the patients are best cared for with care in recovery and long-term health.
Tags
Blog Search
Latest Posts
-
Skin Ulcers Uncovered: Causes, Types, Symptoms, and Healing Options
January 13, 2026 -
Is Coconut Water Safe During Pregnancy? Benefits, Risks & Myths
January 08, 2026 -
Dark Circles Under The Eyes: Causes, Home Remedies and Treatments
December 21, 2025 -
बर्ड फ्लू के लक्षण, कारण, उपचार और बचाव के उपाय जानें
December 04, 2025 -
Best Diet Plan for Menopause Weight Management
November 25, 2025